
.jpg)
Some types of SVT are more common in people who are middle-aged or older. Other things that may increase the risk of supraventricular tachycardia are: It also tends to occur more often in women, particularly during pregnancy, though it may occur in anyone. Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is the most common type of arrhythmia in infants and children. As a result, you may feel lightheaded or dizzy because your brain isn't getting enough blood and oxygen.

The heart doesn't have enough time to fill with blood before the chambers contract. When this happens, the heart rate speeds up very quickly.
Frequent ectopic beats series#
SVT occurs when faulty electrical connections in the heart set off a series of early beats in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). In a typical heart, this heart signaling process usually goes smoothly, resulting in a resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute. When the electrical signals reach the ventricles, the chambers contract and pump blood to the lungs or to the rest of the body. This slight delay allows the ventricles to fill with blood. Next, the heart signals arrive at a cluster of cells called the AV node, where the signals slow down. These electrical signals move across the atria, causing the heart muscles to squeeze (contract) and pump blood into the ventricles. The sinus node sends electrical signals that typically start each heartbeat. The heart's rhythm is controlled by a natural pacemaker (the sinus node) in the right upper chamber (atrium). The heart is made of four chambers - two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).
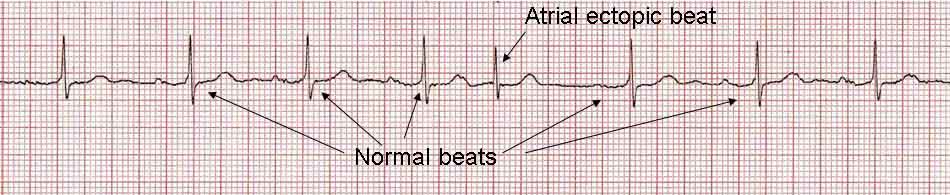
It occurs when faulty electrical connections in the heart set off a series of early beats in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). Supraventricular tachycardia is an irregularly fast heartbeat. Call 911 or your local emergency number if you have an episode of SVT that lasts for more than a few minutes or if you have an episode with any of the following symptoms: Some signs and symptoms of SVT may be related to a serious health condition. However, in extreme cases, an episode of SVT may cause unconsciousness or cardiac arrest.Ĭall your health care provider if you have an episode of a very fast heartbeat for the first time or if an irregular heartbeat lasts longer than a few seconds. Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is generally not life-threatening unless you have heart damage or other heart conditions. If your infant or young child has any of these symptoms, ask your child's care provider about SVT screening.
Frequent ectopic beats skin#
They include sweating, poor feeding, pale skin and a rapid pulse. In infants and very young children, signs and symptoms of SVT may be difficult to identify.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
